Set Custom Fonts
Objective
Main objective of this post is to give you an idea about How to set custom fonts using ttf file in iOS App
Introduction
You can set custom fonts using .ttf file to your iOS Application and then apply those fonts to text controls in your application. The .ttf (True Type Font) file is a font file developed by Apple. Apple and Microsoft use these .ttf files as raster font format. Raster font is a font that can be scaled to any size without losing its quality.
The below information will full fill your requirements to use various .ttf files set custom fonts to your iOS application.
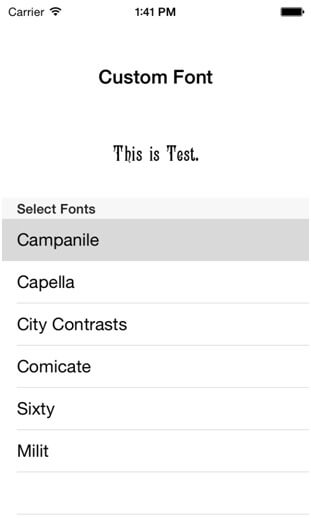
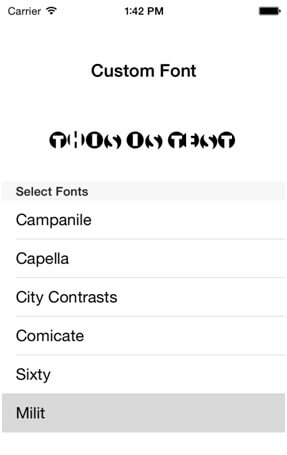
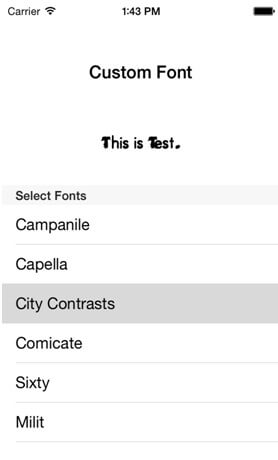
You will get Final Output:
Step 1 Download Custom Fonts
Download various custom fonts .ttf files from web in our demo I have downloaded it from http://www.dafont.com/ttf.d592. Once downloaded drag each font .ttf file inside of the src folder into your project.
Step 2 Custom Fonts
Various files that have used in this demo project describe from following pictures.

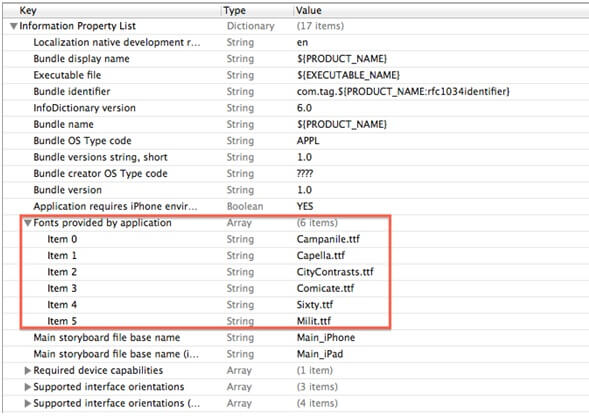
Step 3 Set fonts in Info.plist
Now open .plist file of your project, then add new information property named Fonts provided by application and add following items as name of .ttf file.
You can have brief idea from following figure:
Step 4 Design UI
Prepare your user interface which describe in following figure.

Step 5 Initialised font
Set Data source and delegate of UITableviewController. Write following line of code into viewDidLoad()method of ViewController.m file.
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[superviewDidLoad];
font=[[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"Campanile",@"Capella",@"City Contrasts",@"Comicate",@"Sixty",@"Milit", nil];
}
Step 6 UITableView delegate & datasource methods
Apply following delegate methods into your main ViewController.m file as follows:
-(NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *) tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return [font count];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewcellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
staticNSString *CellIdentifier = @"Cell";
[tableView registerClass:[UITableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath];
[cell setBackgroundColor:[UIColor clearColor]];
NSString *fontName = [font objectAtIndex:[indexPath row]];
[cell.textLabel setText:fontName];
return cell;
}
- (NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewtitleForHeaderInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return @"Select Fonts";
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewdidSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
[lblDemo setFont:[UIFont fontWithName:[font objectAtIndex:indexPath.row] size:20]];
}
If you have got any query related to iOS Set Custom Fonts using in comment them below.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.