AirDrop File Sharing
Objective
The main objective of this blog post is to introduce AirDrop new feature of iOS 7
AirDrop:
AirDrop is a new feature in iOS 7, which is used to share file and data between iOS devices. Using AirDrop we can share photos, videos, location in Maps, application from App Store List, URLs etc. This new feature introduced by Apple works in all iPhone5 models, 4th Generation iPad and iPad mini and 5th generation iPod touch models. In iOS 7 SDK apple bundled UIActivityViewController class which we are using to share file and data. Using this class we just need to pass the objects, which we want to share. This example explains how to use this new UIActivityViewController class for file sharing.
Step 1 Open Xcode Project & select Template
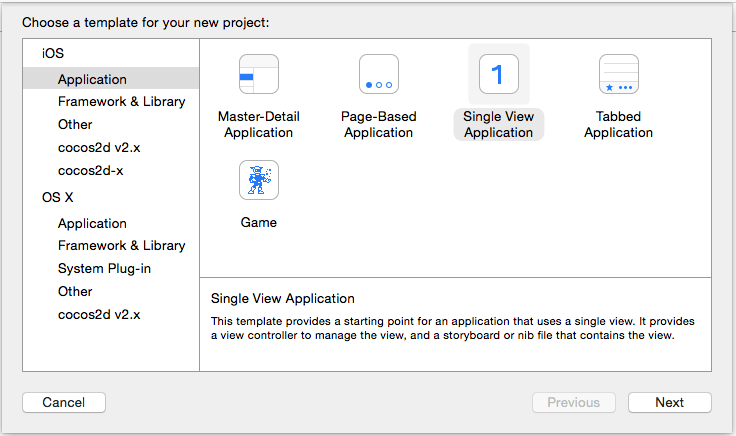
First lets create one XCode project using Single View Application template name it as AirDropDemo as shown in below figure.
Step 2 Fill project data
In the next step enter Product Name as AirDropDemo. And fill all other information as shown in below figure.

Step 3 AirDrop file Sharing
Using AirDrop file sharing is very easy we just need to enable AirDrop from Control Center as shown in below figure. Here if we choose Contacts Only then we can share file with the person who is there in our contacts list. And using everyone option we can share file with any person.
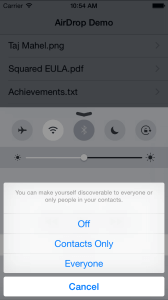
To scan nearby devices AirDrop uses Bluetooth and when using Bluetooth connection is done, device will create an ad-hoc Wi-Fi network to connect devices with each other that provides better speed for data transmission. Here for AirDrop no need to connect devices in Wi-Fi network just we need to on Wi-Fi for data transmission.
Step 4 UITableView Delegate & dataSource Methods
Now in Xcode project lets create one ViewController named it FileListViewController in which we are displaying list of files, which we want to share using below code. Here files is a array of Files name which is created in viewDidLoad method.
#pragma mark - Table view data source
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
// Return the number of sections.
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
// Return the number of rows in the section.
return [files count];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
static NSString *CellIdentifier = @"Cell";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.textLabel.text = [files objectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
return cell;
}
Step 5 Load UIWebView
Next create another ViewController named it DocumentViewController in which we have done the logic to share files using AirDrop. In this class in viewDidLoad method we first load our file in webview using below code.
#pragma mark - View lifecycle
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
NSURL *url = [self generateFileURL:self.documentName];
NSURLRequest *urlRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
[self.webView loadRequest:urlRequest];
}
Here we have used below generateFileURL: function to generate the NSURL from filepath.
- (NSURL *)generateFileURL:(NSString*)filename
Here we have used below generateFileURL: function to generate the NSURL from filepath.
- (NSURL *)generateFileURL:(NSString*)filename
{
NSArray *fileComponents = [filename componentsSeparatedByString:@"."];
NSString *filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:[fileComponents objectAtIndex:0] ofType:[fileComponents objectAtIndex:1]];
return [NSURL fileURLWithPath:filePath];
}
- (IBAction)btnSharePress:(id)sender
Step 6 Sharing Event
Now when user presses on share button we are presenting UIActivityViewController for file sharing. First create UIActivityViewController object with the array of object, which we want to share then present that ViewController.
- (IBAction)btnSharePress:(id)sender
{
NSURL *url = [self generateFileURL:self.documentName];
NSString *string = @"AirDrop File Sharing";
UIActivityViewController *activityViewController = [[UIActivityViewController alloc] initWithActivityItems:@[string, url] applicationActivities:nil];
NSArray*excludedActivities=@[UIActivityTypePostToWeibo,UIActivityTypeAddToReadingList, UIActivityTypePostToFlickr, UIActivityTypePostToVimeo];
activityViewController.excludedActivityTypes = excludedActivities;
[self presentViewController:activityViewController animated:YES completion:^{ }];
}
Step 7 Activity Item which Prevent for Sharing
Using AirDrop if we want to exclude some file sharing option then we can do it by assigning the array of activityItems which we don’t want to include in file sharing option using below code.
NSArray *excludedActivities = @[UIActivityTypePostToWeibo, UIActivityTypeAddToReadingList, UIActivityTypePostToFlickr, UIActivityTypePostToVimeo];
activityViewController.excludedActivityTypes = excludedActivities;
I hope you find this tutorial helpful. If you are facing any issues or have any questions regarding AirDrop File Sharing please feel free to post a reply over here, I would be glad to help you.

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.