UISegmentedControl
Objective
Main objective of this blog post is to give you an idea about how to Use UISegmentedControl in iOS.
You will get Final Output:

Introduction:
UISegmentedControl is a horizontal bar, which is made up of multiple segments. Each segment works as a discrete button and it can display a title or an image. UISegmentedControl is used when you want to show/ hide data based on the selected category in the same view.
For example, you want to display different lists in the same tableView based on the segment selected.
Let’s create a simple app in which the color of the view changes based on the selected segment from UISegmentedControl.
Step 1 Create Xcode Project
Create a new xCode project and select single view application and name it as SegmentedControlDemo.
Step 2 Add Segmented Control
Now go to Main.Storyboard and add the SegmentedControl in the viewController.
Step 3 Design UI
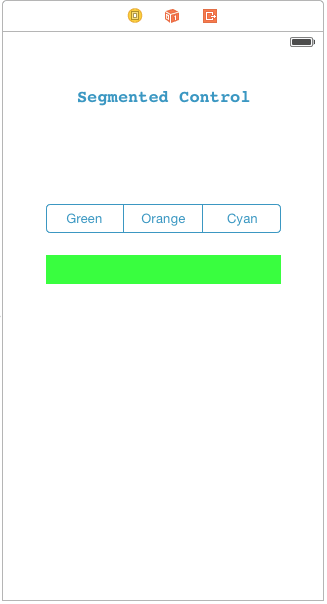
Make user interface like this and give necessary constraints:
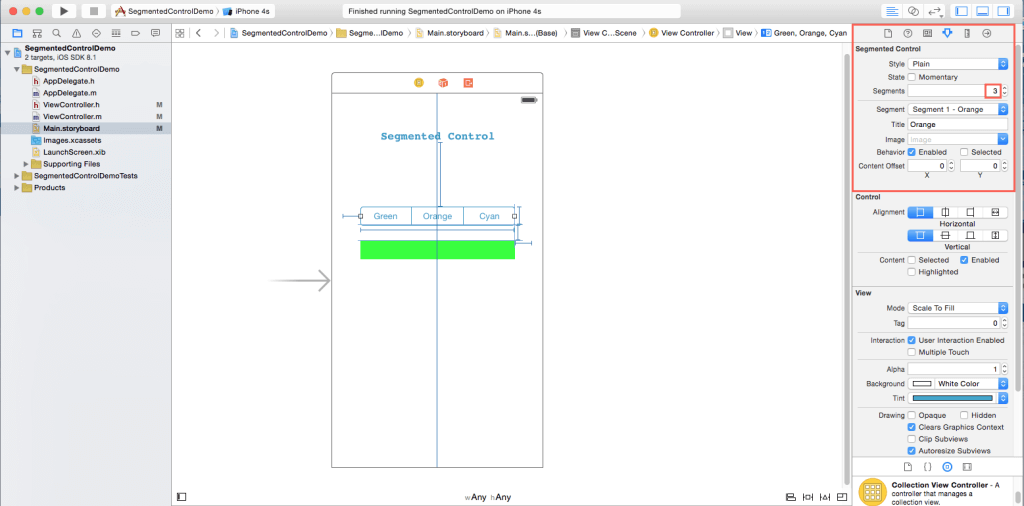
You can change the number of segments in the control from the attributes inspector.
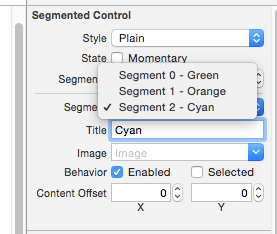
You can also change the names of segments by using following property from attributes inspector.
You can also change the tint and background color from attribute inspector:
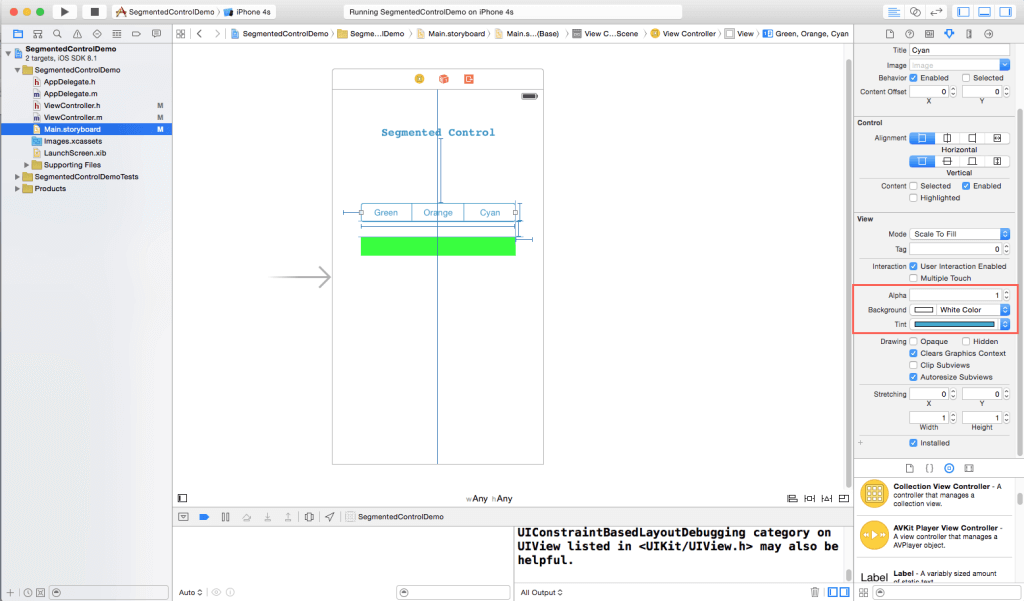
Step 4 Create IBOutlet
Add one UIView below the segmented control. After that make IBOutlets for both segmented control and view. Here we want to change the background color of view based on the selected segment.
To know the current selected segment and based on it to perform the action, make an IBAction for segmented control.
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISegmentedControl *segControlForColor;@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIView *vwToDisplayColor;- (IBAction)segColorBtnTapped:(id)sender;
Step 5 Create IBAction Method
UISegmentedControl has a property called selectedSegmentIndex, which gives the index of current selected segment.
Write below code in the IBAction method that we created earlier:
- (IBAction)segColorBtnTapped:(id)sender {if(segControlForColor.selectedSegmentIndex==0){vwToDisplayColor.backgroundColor=[UIColor greenColor];}else if(segControlForColor.selectedSegmentIndex==1){vwToDisplayColor.backgroundColor=[UIColor orangeColor];}else{vwToDisplayColor.backgroundColor=[UIColor cyanColor];}}
This method changes the color of view based on segment selection.
Step 6 Build & Run the project
Run the project, it will look like this:
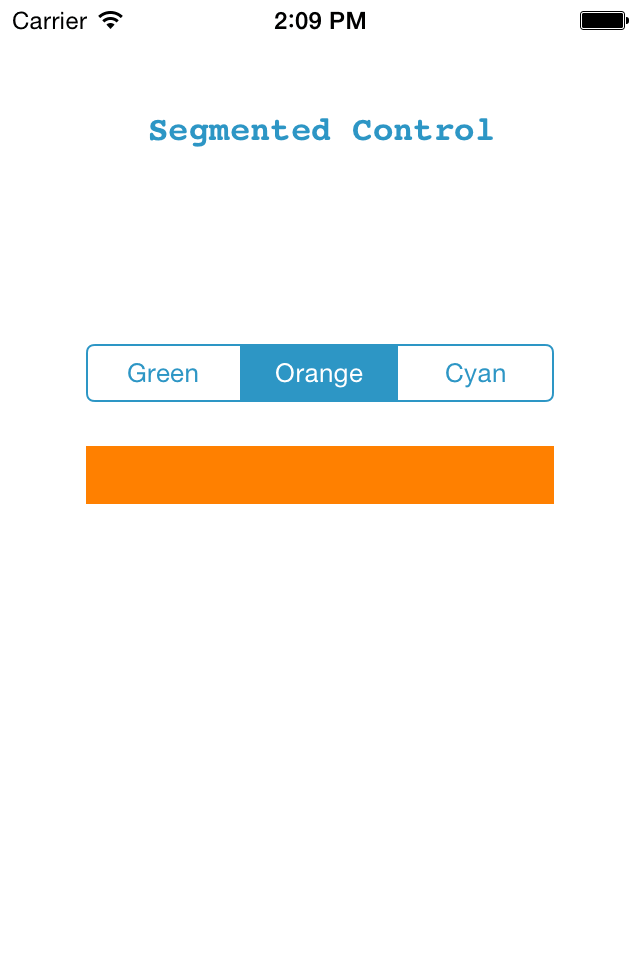
Here, you can see that the color of view is changing based on the selected segment. But suppose you want this type of effect in your segmented control to make it more attractive.
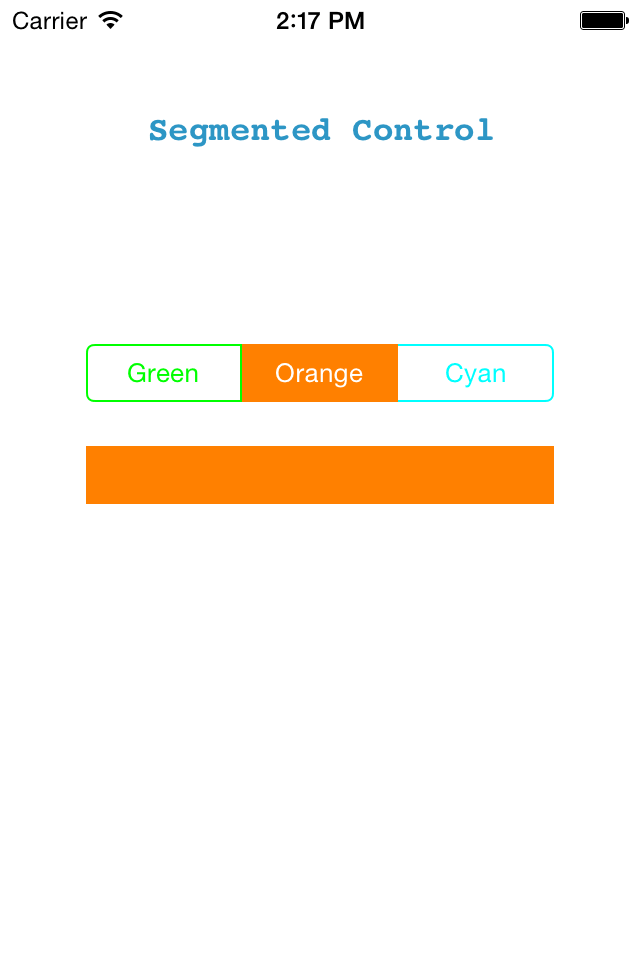
Step 7 Initialized SegmentControl
You may have the question like: How to change the tint color for individual segment?
Write below code in your viewDidLoad method:
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];//To change the tint color[[segControlForColor.subviews objectAtIndex:0]setTintColor:[UIColor cyanColor]];[[segControlForColor.subviews objectAtIndex:1] setTintColor:[UIColor orangeColor]];[[segControlForColor.subviews objectAtIndex:2] setTintColor:[UIColor greenColor]];}
SegmentedControl has a property called subViews that is an array of all the views associated with the segments. Here, index 0 means back most view in the segmented control.
tintColor is also a property of this control which is used to set the tint color for that particular object from subView array.
I hope you will find this blog post very useful. While working with UISegmentedControl in iOS. Let me know in comment if you have any questions regarding in IOS. I will reply you ASAP
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.