The material style provides an extra designing effect to tab bar at the bottom of screen. The material design makes you to switch among the different screens. The tab screen components are not mounted until the screens are first focused.
To use the material design navigator, install react-navigation-material-bottom-tabs library as:
- npm install react-navigation-material-bottom-tabs react-native-paper
This library uses the BottomNavigation component from react-native-paper.
It is also require to install react-native-vector-icons.
- createMaterialBottomTabNavigator(RouteConfigs, MaterialBottomTabNavigatorConfig);
Example to Create Material Bottom Tab Navigation
In this example, we implement the material bottom tab navigator to highlights the active tab's icons and its title. The rest of tab display only icon without the title. To use material designs, import the createMaterialBottomTabNavigator function from react-navigation-material-bottom-tabs library.
App.js
- import React from 'react';
- import {StyleSheet, Text, View,Button} from 'react-native';
- import { createBottomTabNavigator, createAppContainer} from 'react-navigation';
- import { createMaterialBottomTabNavigator } from 'react-navigation-material-bottom-tabs';
- import Icon from 'react-native-vector-icons/Ionicons';
- class HomeScreen extends React.Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <Text>Home Screen</Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- class ProfileScreen extends React.Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <Text>Profile Screen</Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- class ImageScreen extends React.Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <Text>Image Screen</Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- class CartScreen extends React.Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <Text>Cart Screen</Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- flex: 1,
- justifyContent: 'center',
- alignItems: 'center'
- },
- });
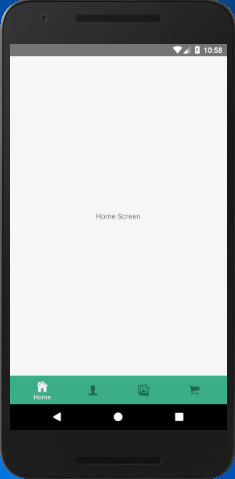
- const TabNavigator = createMaterialBottomTabNavigator(
- {
- Home: { screen: HomeScreen,
- navigationOptions:{
- tabBarLabel:'Home',
- tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
- <View>
- <Icon style={[{color: tintColor}]} size={25} name={'ios-home'}/>
- </View>),
- }
- },
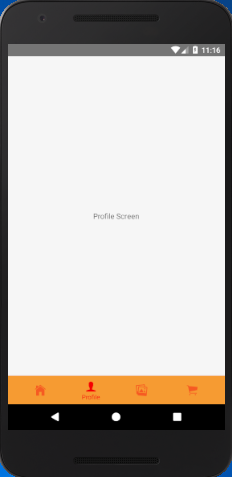
- Profile: { screen: ProfileScreen,
- navigationOptions:{
- tabBarLabel:'Profile',
- tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
- <View>
- <Icon style={[{color: tintColor}]} size={25} name={'ios-person'}/>
- </View>),
- activeColor: '#f60c0d',
- inactiveColor: '#f65a22',
- barStyle: { backgroundColor: '#f69b31' },
- }
- },
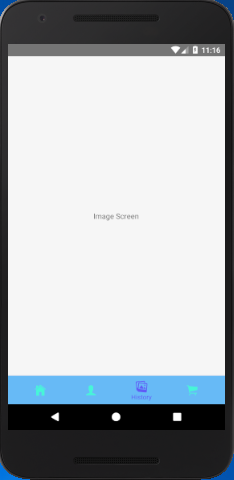
- Image: { screen: ImageScreen,
- navigationOptions:{
- tabBarLabel:'History',
- tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
- <View>
- <Icon style={[{color: tintColor}]} size={25} name={'ios-images'}/>
- </View>),
- activeColor: '#615af6',
- inactiveColor: '#46f6d7',
- barStyle: { backgroundColor: '#67baf6' },
- }
- },
- Cart: {
- screen: CartScreen,
- navigationOptions:{
- tabBarLabel:'Cart',
- tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
- <View>
- <Icon style={[{color: tintColor}]} size={25} name={'ios-cart'}/>
- </View>),
- }
- },
- },
- {
- initialRouteName: "Home",
- activeColor: '#f0edf6',
- inactiveColor: '#226557',
- barStyle: { backgroundColor: '#3BAD87' },
- },
- );
-
- export default createAppContainer(TabNavigator);
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.