The FlatList component displays the similar structured data in a scrollable list. It works well for large lists of data where the number of list items might change over time. The FlatList shows only those renders elements which are currently displaying on the screen, not all the elements of the list at once.
The FlatList component takes two required props: data and renderItem.
The data is the source of elements for the list, and renderItem takes one item from the source and returns a formatted component to render.
To implement the FlatList component, we need to import FlatList from 'react-native' library.
React Native FlatList Example
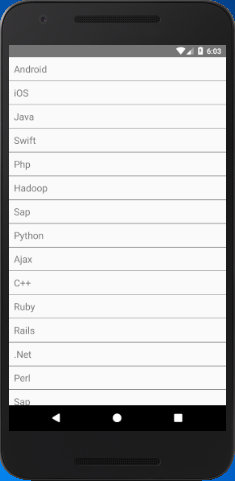
In this example, we provide hardcoded elements to data prop. Each element in the data props is rendered as a Text component.
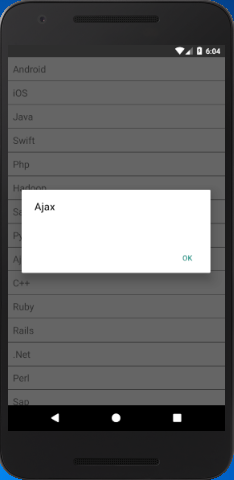
The ItemSeparatorComponent prop of FlatList is used to implement the separator between the elements of the list. To perform the click event on list items, we use onPress prop to Text.
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { AppRegistry, FlatList,
- StyleSheet, Text, View,Alert } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class FlatListBasics extends Component {
-
- renderSeparator = () => {
- return (
- <View
- style={{
- height: 1,
- width: "100%",
- backgroundColor: "#000",
- }}
- />
- );
- };
-
- getListViewItem = (item) => {
- Alert.alert(item.key);
- }
-
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <FlatList
- data={[
- {key: 'Android'},{key: 'iOS'}, {key: 'Java'},{key: 'Swift'},
- {key: 'Php'},{key: 'Hadoop'},{key: 'Sap'},
- {key: 'Python'},{key: 'Ajax'}, {key: 'C++'},
- {key: 'Ruby'},{key: 'Rails'},{key: '.Net'},
- {key: 'Perl'},{key: 'Sap'},{key: 'Python'},
- {key: 'Ajax'}, {key: 'C++'},{key: 'Ruby'},
- {key: 'Rails'},{key: '.Net'},{key: 'Perl'}
- ]}
- renderItem={({item}) =>
- <Text style={styles.item}
- onPress={this.getListViewItem.bind(this, item)}>{item.key}</Text>}
- ItemSeparatorComponent={this.renderSeparator}
- />
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
-
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- flex: 1,
- },
- item: {
- padding: 10,
- fontSize: 18,
- height: 44,
- },
- })
-
-
- AppRegistry.registerComponent('AwesomeProject', () => FlatListBasics);
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.