While creating an app containing multiple screens, then sometimes it is required to pass value between one screen to another. This can be achieved by using this.props.navigation.navigate() function.
This function is used to navigate between the different screens.
Example
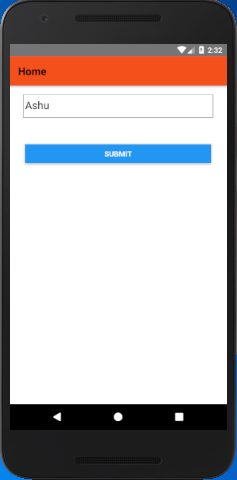
In this example, we will input the value in the first screen and get it into the second screen.
The value (param) is passed as an object in the first screen to the navigation.navigate function as:
- this.props.navigation.navigate('RouteName', { })
The same value (param) is read in the second screen as:
- this.props.navigation.getParam(paramName, defaultValue)
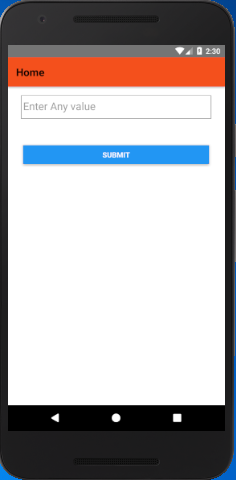
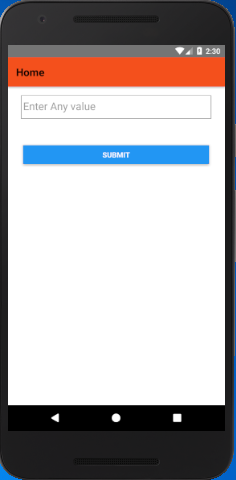
Create a HomeScreen.js file and add a TextInput component for input value and a Button to submit. The TextInput component has an onChangeText prop which takes a function which is to be called whenever the text changed.
HomeScreen.js
- import React from 'react';
-
- import { StyleSheet, View, Button, TextInput } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class HomeScreen extends React.Component {
-
- constructor(props) {
-
- super(props);
- this.state = {
- username: '',
- };
- }
- static navigationOptions = {
- title: 'Home',
- headerStyle: {
- backgroundColor: '#f4511e',
- },
-
- headerTitleStyle: {
- fontWeight: 'bold',
- },
- };
-
- render() {
- const { navigate } = this.props.navigation;
- return (
-
- <View style={styles.container}>
- {}
- <TextInput
- value={this.state.username}
- onChangeText={username => this.setState({ username })}
- placeholder={'Enter Any value'}
- style={styles.textInput}
- />
- <View style={styles.buttonStyle}>
- <Button
- title="Submit"
-
- onPress={() =>
- this.props.navigation.navigate('Profile', {
- userName: this.state.username,
- otherParam: '101',
- })
- }
- />
- </View>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- flex: 1,
- backgroundColor: '#fff',
- alignItems: 'center',
- padding: 16,
- },
- textInput: {
- height: 45,width: "95%",borderColor: "gray",borderWidth: 1,fontSize:20,
- },
- buttonStyle:{
- width: "93%",
- marginTop: 50,
- backgroundColor: "red",
- }
- });
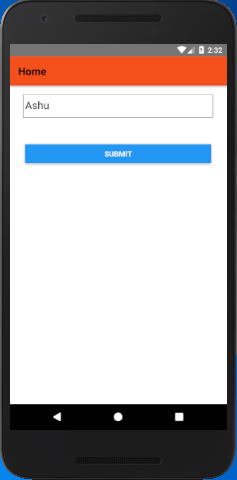
In the above code userName: this.state.username, store the value input into the TextInput component and otherParam: '101' directly assign a value. On clicking the Button userName and otherParam is passed to Profile screen.
ProfileScreen.js
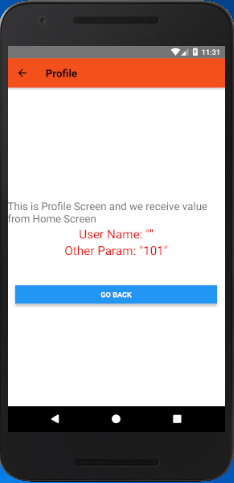
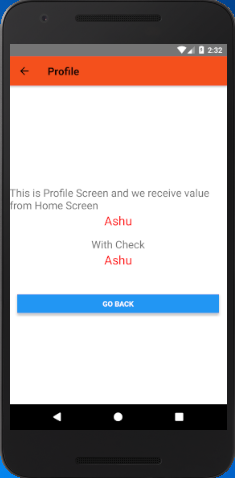
In this screen, we receive the value of userName and otherParam using navigation.getParam('paramValue', default value) and stored into object user_name and other_param respectively. The value of JavaScript object is converted to string using JSON.stringify(object) function.
- import React from 'react';
- import { StyleSheet, View, Text, Button } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class ProfileScreen extends React.Component {
- static navigationOptions = {
- title: 'Profile',
- headerStyle: {
- backgroundColor: '#f4511e',
- },
-
- headerTitleStyle: {
- fontWeight: 'bold',
- },
- };
- render() {
- {
- }
- const { navigation } = this.props;
- const user_name = navigation.getParam('userName', 'NO-User');
- const other_param = navigation.getParam('otherParam', 'some default value');
- return (
- <View style={{ flex: 1, alignItems: "center", justifyContent: "center" }}>
- <Text style={{ marginTop: 16,fontSize: 20,}}>
- This is Profile Screen and we receive value from Home Screen
- </Text>
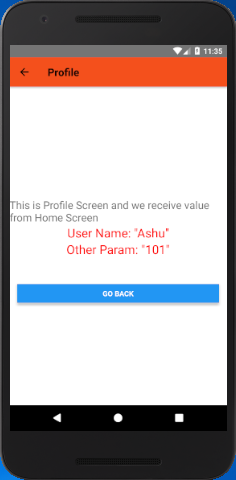
- <Text style={styles.textStyle}>User Name: {JSON.stringify(user_name)}</Text>
- <Text style={styles.textStyle}>Other Param: {JSON.stringify(other_param)}</Text>
- <View style={styles.buttonStyle}>
- <Button
- title="Go back"
- onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}
- />
- </View>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- textStyle: {
- fontSize: 23,
- textAlign: 'center',
- color: '#f00',
- },
-
- buttonStyle:{
- width: "93%",
- marginTop: 50,
- backgroundColor: "red",
- }
- });
App.js
Create the App.js file as it is the entry point of the app and imports the HomeScreen and ProfileScreen. The HomeScreen set as the first screen using the initialRouteName.
- import React from 'react';
- import {createStackNavigator,createAppContainer} from 'react-navigation';
- import HomeScreen from './HomeScreen';
- import ProfileScreen from './ProfileScreen';
-
- const AppNavigator = createStackNavigator(
- {
- Home: HomeScreen,
- Profile: ProfileScreen
- },
- {
- initialRouteName: "Home"
- }
- );
- export default createAppContainer(AppNavigator);
Output:
We also send and receive the parameters into JSON such as:
HomeScreen.js
- onPress={() =>
- navigate('Profile', {
- JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item: this.state.username,
- })
- }
ProfileScreen.js
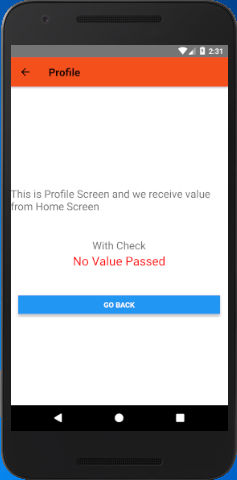
This screen read the value in two ways without checking.
- {this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item}
Or checking the input value is null or not
- {this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item
- ? this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item
- : 'No Value Passed'}
- <Text style={styles.textStyle}>
- {this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item}
- </Text>
- <Text style={{ marginTop: 16,fontSize: 20, }}>With Check</Text>
- {
- }
- <Text style={styles.textStyle}>
- {this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item
- ? this.props.navigation.state.params.JSON_ListView_Clicked_Item
- : 'No Value Passed'}
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.