In the previous tutorial of
ProgressBarAndroid we learn how to display the default progress bar. However, we can also customize the progress bar using
Animated class.
React Native ProgressBar with Animated Example
To create an animated progessbar we need to import theAnimated class. Add Animated.View and Animated.Text component inside View. Initialize a variable progress status to 0 and call the onAnimate() method. This method will invoked when the screen will completely loaded (componentDidMount() calls). Add a listener on onAnimate() method which updates the progress status.
App.js
import React, {Component} from 'react'; - import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View, Animated} from 'react-native';
-
- export default class App extends Component {
- state={
- progressStatus: 0,
- }
- anim = new Animated.Value(0);
- componentDidMount(){
- this.onAnimate();
- }
- onAnimate = () =>{
- this.anim.addListener(({value})=> {
- this.setState({progressStatus: parseInt(value,10)});
- });
- Animated.timing(this.anim,{
- toValue: 100,
- duration: 50000,
- }).start();
- }
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <Animated.View
- style={[
- styles.inner,{width: this.state.progressStatus +"%"},
- ]}
- />
- <Animated.Text style={styles.label}>
- {this.state.progressStatus }%
- </Animated.Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- width: "100%",
- height: 40,
- padding: 3,
- borderColor: "#FAA",
- borderWidth: 3,
- borderRadius: 30,
- marginTop: 200,
- justifyContent: "center",
- },
- inner:{
- width: "100%",
- height: 30,
- borderRadius: 15,
- backgroundColor:"green",
- },
- label:{
- fontSize:23,
- color: "black",
- position: "absolute",
- zIndex: 1,
- alignSelf: "center",
- }
- });
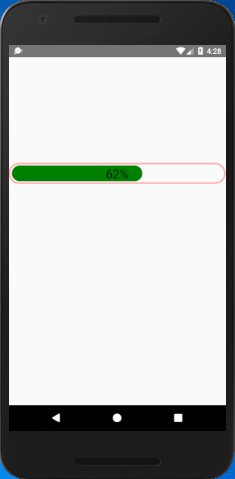
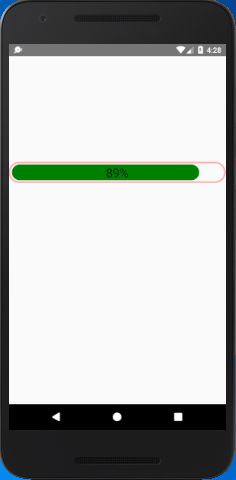
The progress status of progress bar is updated in the interval of per 0.5 second (50000 microseconds). At the same time the width of progress bar is determined by progress status, and its status is set into Animated.Text component.
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.