React Native Switch is a Boolean control component which sets its value to true or false. It has an onValueChange callback method that updates its value prop. If the value prop is not changed, the Switch component continues supplied the value prop instead of the expected result of any user actions.
Props of Switch
| Props | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled | It is a Boolean property, if it is set to true then it cannot be toggled to switch. Its default value is false. |
| trackColor | It is used to customize the color for switch track. |
| ios_backgroundColor | It set the custom background color in iOS. The background can be visible either when the switch value is disabled or when the switch is false. |
| onValueChange | It invoked when the switch value is changed. |
| testID | It is used to locate this view in end-to-end tests. |
| thumbColor | It colors the foreground switch grip. When it is set to iOS, the switch grip will lose its drop shadow. |
| tintColor | It sets the border color on iOS and background color on Android when the switch is turned off. This property is deprecated; use trackColor at the place of it. |
| value | It is the value of switch. When it is set to true, it turns on. The default value is false. |
React Native Switch Example
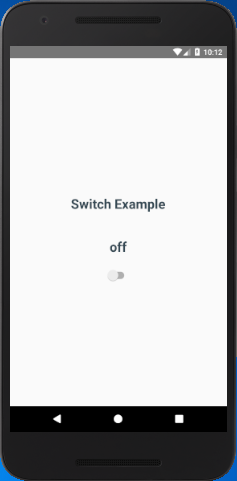
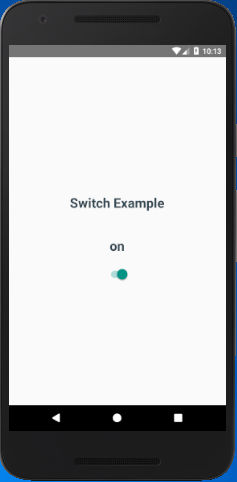
In this example, we initialy set the Switch value to false and display a Text with 'off'. When the value of Switch change to true by calling onValueChange the Text component is reset to 'on'.
App.js
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.