React Native Tab Navigation is the most common navigation style in the mobile applications. The Tab Navigation is tabbed at the bottom of the screen or on the top below the header or sometimes as a header. It is used to switch between different route screens.
To create Tab-based navigation, import createBottomTabNavigator and createAppContainer in the root functions of the react-navigation library.
Bottom Tab Navigator Configuration
There are various configurable props of BottomTabNavigator. Some of them are:
| Prop | Description |
|---|---|
| initialRouteName | It defines the initial tab route when the app first loads. |
| order | It is an array of route screen, which sets the order of the tabs. |
| paths | It provides the mapping of route screen to path config, which overrides the paths set in the routeConfigs. |
| lazy | Setting it as {true} makes the tab to rendered when the tab becomes active for the first time. If it is set to false, all tabs are rendered immediately. Its default value is true. |
| tabBarComponent | It overrides the component, which is used as the tab bar. It is optional. |
| tabBarOptions | It is an object of the following properties: activeTintColor, activeBackgroundColor, inactiveTintColor , inactiveBackgroundColor, showLabel, showIcon, style, labelStyle, tabStyle, allowFontScaling. |
Tab - based navigation Example
Create the two classes named as HomeScreen and ProfileScreen. Register these classes in createBottomTabNavigator function with Home and Profile tab respectively.
Output:
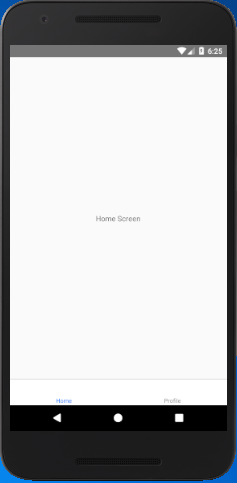
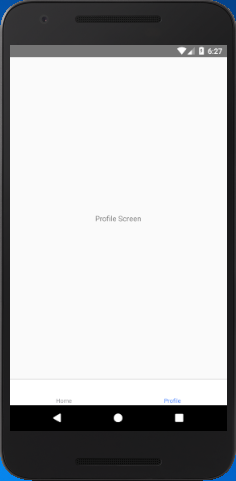
If we set the initialRouteName: "Profile" then, it loads the "ProfileScreen" as an initial route tab.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.