Deep Linking Your React Native App
In this post, I’ll quickly walk through how to add deep linking to a React Native app for both iOS and Android using React Navigation.

The final code for this tutorial is located here.
There are many cases where providing a url to transition a user to a specific point in your app on load makes a lot of sense.
For example, say you have a person’s profile, and you want to provide a link somewhere on the web or in another app, so that when the user clicks on a link, we not only open the app but also navigate to the exact point in the app that we want to go.
This is what deep linking is, and this is what we will be walking through in this post.
Linking will provide for us an API that will allow us to listen for an incoming linked url, and then we can handle the url like
componentDidMount() {
Linking.addEventListener('url', this.handleOpenURL);
}componentWillUnmount() {
Linking.removeEventListener('url', this.handleOpenURL);
}handleOpenURL(event) {
console.log(event.url);
const route = e.url.replace(/.*?:\/\//g, '');
// do something with the url, in our case navigate(route)
}
When a user in an external app or website clicks on one of our links, we will open in our new app and navigate to the intended url:
peopleapp://people/0
peopleapp://people/1
peopleapp://people/2
..etcThat will navigate to the people route, and then show a person based on the id.
Let’s get started by creating a new React Native app and adding react-navigation
react-native init PeopleAppOnce installed, cd into the new directory and install react-navigation using npm or yarn
npm i -s react-navigationor
yarn add react-navigationNow that we have our app and some navigation, let’s create a router and two views: a home view and the people view.
touch router.js home.js people.jsNow, let’s go into index.ios.js / index.android.js and import the router will will create next.
// index.ios.js or index.android.jsimport { AppRegistry } from 'react-native';import Router from './router';AppRegistry.registerComponent('PeopleApp', () => Router);
Now, we’ll go ahead and create the router. In router.js
// router.jsimport React from 'react';import {
AppRegistry,
Text,
} from 'react-native';import { StackNavigator } from 'react-navigation';
import Home from './home';
import People from './people';const Router = StackNavigator({
Home: { screen: Home },
People: { screen: People },
});export default Router;
Then, we’ll create the Home component. In home.js
import React from 'react';
import { Platform, Text, Linking } from 'react-native';class Home extends React.Component {
static navigationOptions = { // A
title: 'Home',
};componentDidMount() { // B
if (Platform.OS === 'android') {
Linking.getInitialURL().then(url => {
this.navigate(url);
});
} else {
Linking.addEventListener('url', this.handleOpenURL);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() { // C
Linking.removeEventListener('url', this.handleOpenURL);
} handleOpenURL = (event) => { // D
this.navigate(event.url);
} navigate = (url) => { // E
const { navigate } = this.props.navigation;
const route = url.replace(/.*?:\/\//g, '');
const id = route.match(/\/([^\/]+)\/?$/)[1];
const routeName = route.split('/')[0];
if (routeName === 'people') {
navigate('People', { id, name: 'chris' })
};
} render() {
return <Text>Hello from Home!</Text>;
}}export default Home;
A. We declare a title using static navigationOptions for react-navigation to show a title when we are on this route.
B. If we are on Android, we immediately call the navigate method passing in the url. If we are on iOS, We add an event listener to call handleOpenUrl when an incoming link is detected.
C. We delete the Linking listener on componentWillUnmount
D. When handleOpenURL is called, we pass the event url to the navigate method.
E. We first parse the url to get the id and route name. We then check to see if the route name is equal to people, and if so we navigate to the People component, passing the id as a prop.
Now we can go to people.js and create the component there that will be showing a person based on a route id. In people.js
import React from 'react';
import { Text, Image, View, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';const people = { // A
0: {
name: 'Leela',
image: 'http://vignette1.wikia.nocookie.net/en.futurama/images/d/d4/Turanga_Leela.png/revision/latest?cb=20150218013044',
},
1: {
name: 'Bender',
image: 'https://vignette2.wikia.nocookie.net/en.futurama/images/4/43/Bender.png/revision/latest?cb=20150206072725',
},
2: {
name: 'Amy',
image: 'https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4sCtTq7K3yI/hqdefault.jpg',
},
3: {
name: 'Fry',
image: 'http://www.supergrove.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/fry-futurama-22-which-robot-from-quotfuturamaquot-are-you.jpg',
}
}class People extends React.Component {
static navigationOptions = {
title: 'People',
};
render() {
const { id } = this.props.navigation.state.params; // B
if (!people[id]) return <Text>Sorry, no data exists for this user</Text>return ( // C
<View>
<Text style={styles.text}>{people[id].name}</Text>
<Image
resizeMode="contain"
style={styles.image}
source={{ uri: people[id].image }}
/>
</View>
)
}
}const styles = StyleSheet.create({
text: {
margin: 19,
fontSize: 22,
},
image: {
width: 400,
height: 400,
},
});export default People;
A. We create a hardcoded object with some information about a few people, including only their name and image with a corresponding id key.
B. We destructure the id prop that we will be receiving. If no user exists for this id, we display a message.
C. We use the id to reference the correct person, displaying their image and name.
Ok, now that we have all of our basic code set up, we now need to configure both iOS and Android to enable deep linking.
Configuring iOS
Step 1. Add URL type to info.plist
- Open
info.plistand at the top of the file, create a new property calledURL types
2. Expand item 0 (zero) and choose URL Schemes.
3. Give item 0 the name you would like your app to be linkable as. In our case, I chose peopleapp as the name.
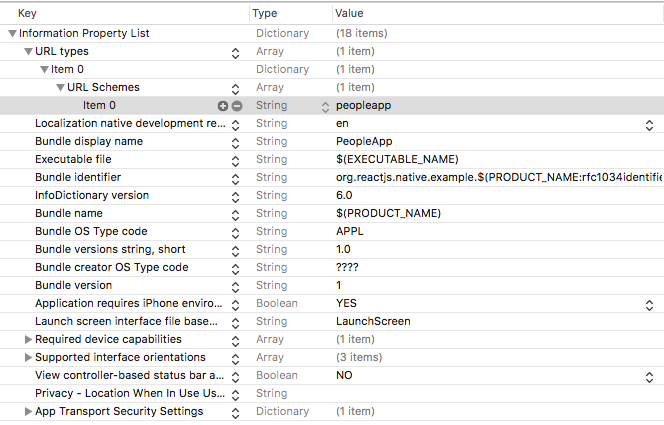
peopleappwill be what we use to identify the app. Once this identifier is set up, we will be able to reference it outside of the application in web browsers and other apps, like so:peopleapp://someurl/someotherinfo/…
Step 2. Add the following code to AppDelegate.m
Below last existing import add this import:
#import <React/RCTLinkingManager.h>Directly below @implementation AppDelegate add this code:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application openURL:(NSURL *)url
sourceApplication:(NSString *)sourceApplication annotation:(id)annotation
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application openURL:url
sourceApplication:sourceApplication annotation:annotation];
}
// Only if your app is using [Universal Links](https://developer.apple.com/library/prerelease/ios/documentation/General/Conceptual/AppSearch/UniversalLinks.html).
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application continueUserActivity:(NSUserActivity *)userActivity
restorationHandler:(void (^)(NSArray * _Nullable))restorationHandler
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application
continueUserActivity:userActivity
restorationHandler:restorationHandler];
}Now your final AppDelegate.m should look something like this linked Github gist.
Now we should be able to open up safari or chrome and pass in the following url:
peopleapp://people/0And the app should redirect on load to the correct route, showing the correct person’s info!

Configuring Android
First, we need to open our Manifest file and add the app name we will want to be referencing, in our case peopleapp.
In android/app/src/main, open AndroidManifest.xml and add the following intent filter below the last intent filter already listed, within the <activity> tag:
<intent-filter android:label="filter_react_native">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="peopleapp" android:host="people" /> // A
</intent-filter>Here is an idea of how your AndroidManifext.xml should now look.
The <data> tag specifies the URL scheme which resolves to the activity in which the intent filter has been added. In this example the intent filter accepts URIs that begin with
peopleapp://people. To learn more about this configuration, check out this documentation.
That is all we need as far as configuration goes. To test this out, open Android Studio. Open Run -> Edit Configurations and change the launch options to URL, passing in the following url: peopleapp://people/1

Now when we run the app, we should see Bender!
The final code for this example can be found here.
My Name is Sanjay Vaghasiya . I am a software consultant and trainer and the founder of React Native Training where we do React Native consulting as well as teach developers at top companies around the world how to quickly get up and running with React Native.
If you like React and React Native, please comment,
If you enjoyed this article, please recommend and share it! Thanks for your time, Sanjay.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.