React Native Alert is an API which is used to display an alert dialog with specified title and message. It uses an alert() method to prompt an alert dialog. This Alert dialog provides three different lists of buttons (combination of neutral, negative, and positive) to perform action. Pressing any of these buttons calls the onPress callback method and dismiss the alert. By default, Alert has only a positive (OK) button.
The Alert that prompts to enter some information is created using AlertIOS. It is only supported in iOS.
React Native Alert in iOS
In iOS, we can specify number of buttons. Each buttons can be separately specify a style, which is one of default, cancel, or destructive.
React Native Alert in Android
In Android, the Alert button can be specified with mainly three buttons. These buttons are a neutral, negative and a positive button:
Alert buttons are specified in three different combinations. These are:
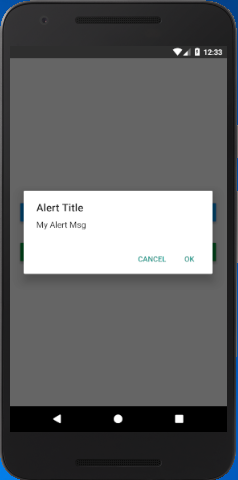
- If we specify only one button, it will be the 'positive' one (such as 'OK').
- If we specify two buttons, it will be 'negative' and 'positive' (such as 'Cancel', 'OK').
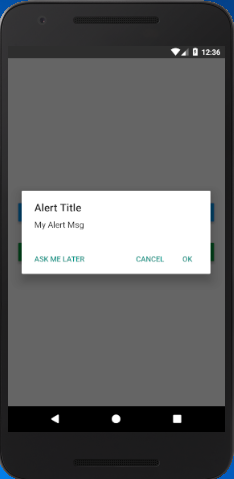
- Specifying three buttons means 'neutral', 'negative', 'positive' (such as 'Later', 'Cancel', 'OK').
In Android, the alerts are by default dismissed by clicking outside the alert dialog. The dismiss event can be handled by using an optional parameter, with an onDismiss callback property { onDismiss: () => {} }. However, we can disable the dismissing property by using the property {cancelable: false}.
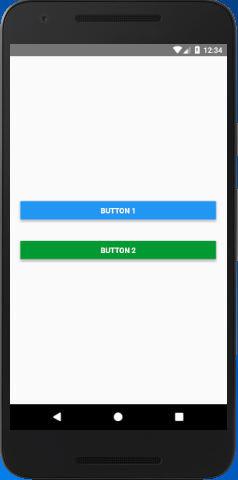
React Native Alert Example
In this example, we create two alerts on two buttons. One alert contains two options button without cancelable. Other alert contains three options button with cancelable false.
App.js
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.