React Native AsyncStorage is a simple, unencrypted, asynchronous, persistent, storage system which stores the data globally in the app. It store data in the form of a key-value pair.
React Native recommended to use abstraction on top of AsyncStorage instead of AsyncStorage directly as it operates globally.
On iOS, AsyncStorage is approved by the native code. The iOS native code stores the small values in a serialized dictionary and the larger values in separate files.
On Android, AsyncStorage will use either SQLite or RocksDB based on the availability.
To use the AsyncStorage, import AsyncStorage library as:
- import {AsyncStorage} from 'react-native';
Persist Data:
React Native AsyncStorage saves the data using setItem() method as:
- AsyncStorage.setItem('key', 'value');
Example of persisting the single value:
- let name = "Michal";
- AsyncStorage.setItem('user',name);
Example of persisting multiple values in an object:
- let obj = {
- name: 'Michal',
- email: 'michal@gmail.com',
- city: 'New York',
- }
- AsyncStorage.setItem('user',JSON.stringify(obj));
Fetch Data:
React Native AsyncStorage fetches the saved data using getItem() method as:
- await AsyncStorage.getItem('key');
Example to fetch the single value:
- await AsyncStorage.getItem('user');
Example to fetch value from an object:
- let user = await AsyncStorage.getItem('user');
- let parsed = JSON.parse(user);
- alert(parsed.email);
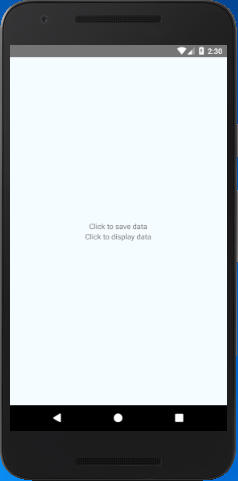
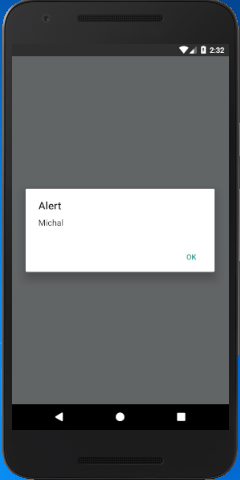
React Native AsyncStorage Example 1
In this example, we create the two TouchableOpacity components, one for saving the data and another for retrieving. From first TouchableOpacity component call the savaData() method to save data and from the second TouchableOpacity component call the displayData() method to fetch data.
- import React, {Component} from 'react';
- import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text,
- View,TouchableOpacity, AsyncStorage,
- } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class App extends Component<Props> {
- saveData(){
- let name = "Michal";
- AsyncStorage.setItem('user',name);
- }
- displayData = async ()=>{
- try{
- let user = await AsyncStorage.getItem('user');
- alert(user);
- }
- catch(error){
- alert(error)
- }
- }
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <TouchableOpacity onPress ={this.saveData}>
- <Text>Click to save data</Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- <TouchableOpacity onPress ={this.displayData}>
- <Text>Click to display data</Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
-
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- flex: 1,
- justifyContent: 'center',
- alignItems: 'center',
- backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
- },
- });
Output:
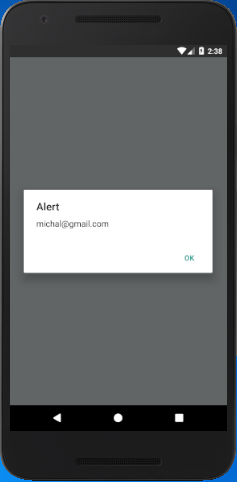
React Native AsyncStorage Example 2
In this example, we will save the multiple values in the form if JSON object using JSON.stringify(). The JSON.stringify() takes the JavaScript object and convert them into JSON string. On the other hand, JSON.parse() method is used to fetch the AsyncStorage data. This method takes the JSON string and converts it into a JavaScript object before they are returned.
- import React, {Component} from 'react';
- import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text,
- View,TouchableOpacity, AsyncStorage,
- } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class App extends Component<Props> {
- saveData(){
-
- let obj = {
- name: 'Michal',
- email: 'michal@gmail.com',
- city: 'New York',
- }
-
- AsyncStorage.setItem('user',JSON.stringify(obj));
- }
- displayData = async ()=>{
- try{
- let user = await AsyncStorage.getItem('user');
- let parsed = JSON.parse(user);
- alert(parsed.email);
- }
- catch(error){
- alert(error)
- }
- }
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <TouchableOpacity onPress ={this.saveData}>
- <Text>Click to save data</Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- <TouchableOpacity onPress ={this.displayData}>
- <Text>Click to display data</Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
-
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container: {
- flex: 1,
- justifyContent: 'center',
- alignItems: 'center',
- backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
- },
- });
Output:
AsyncStorage Methods
There are various methods of React Native AsyncStorage class which are described below:
Methods
setItem()
- static setItem(key: string, value: string, [callback]: ?(error: ?Error)=>void)
The
setItem() sets the value for a
key and invokes a callback upon compilation. It returns a Promise object.
getItem()
- static getItem(key: string, [callback]: ?(error: ?Error, result: ?string)) =>void)
The
getItem() fetches an item from a
key and invokes a callback upon completion. It returns a Promise object.
removeItem()
- static removeItem(key: string, [callback]: ?(error: ?Error) => void)
The
removeItem() removes an item for a
key and invokes a callback upon compilation. It returns a Promise object.
mergeItem()
- static mergeItem(key: string, value: string, [callback]: ?(error: ?Error) => void)
The
mergeItem() merges the existing key's value with the input value and assuming both values are stringified JSON. It returns a Promise object.
NOTE: This method is not supported by all the native implementations.
clear()
- static clear([callback]: ?(error: ?Error) => void)
The
clear() method erases all AsynchStorage from all clients, libraries, etc. It is suggested that don't call this, instead of this you may use
removeItem or
multiRemove to clear only your app's keys. It returns the Promise object.
getAllKeys()
- static getAllKeys([callback]: ?(error: ?Error, keys: ?Array<string>) => void)
It gets all the keys which are known to your app, for all callers, libraries, etc. It returns a Promise object.
flushGetRequests()
- static flushGetRequests(): [object Object]
It flushes any pending request using a single batch call to get the data.
multiGet()
- static multiGet(keys: Array<string>, [callback]: ?(errors: ?Array<Error>, result: ?Array<Array<string>>) => void)
This method allows you to batch fetching of items given in an array of key inputs. The callback method will be invoked with an array of corresponding key-value pairs found:
- multiGet(['k1', 'k2'], cb) -> cb([['k1', 'val1'], ['k2', 'val2']])
The method returns a Promise object.
multiSet()
- static multiSet(keyValuePairs: Array<Array<string>>, [callback]: ?(errors: ?Array<Error>) => void)
This method is used as a batch operation to store multiple key-value pairs. After the completion of operations, you will get a single callback with any errors:
- multiSet([['k1', 'val1'], ['k2', 'val2']], cb);
The method returns a Promise object.
multiRemove()
- static multiRemove(keys: Array<string>, [callback]: ?(errors: ?Array<Error>) => void)
This method calls the batch deletion of all keys in the key array. It returns a Promise object.
multiMerge()
- static multiMerge(keyValuePairs: Array<Array<string>>, [callback]: ?(errors: ?Array<Error>) => void)
It executes the batch of operation to merge existing and new values for a given set of keys. It assumes that the values are stringified JSON. It returns a Promise object.
Note: This method is not supported by all native implementations.


Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.