React Native Flexbox is an algorithm to specify the layout of component's children. It provides a consistent layout on different screen sizes.
Property of Flexbox
Flexbox provides three main properties to achieve the desired layout. These properties are: flexDirection, justifyContent, and alignItems.
| Property | Values | Description |
|---|
| flexDirection | 'column', 'row' | Used to align its elements vertically or horizontally. |
| justifyContent | 'center', 'flex-start', 'flex-end', 'space-around', 'space-between' | Used to distribute the elements inside the container. |
| alignItems | 'center', 'flex-start', 'flex-end', 'stretched' | Used to distribute the element inside the container along the secondary axis (opposite to flexDirection). |
React Native Flex Direction
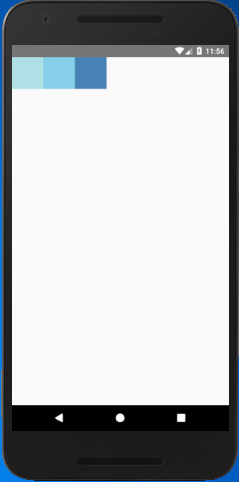
The flexDirection adds the style to the component in a primary axis of its layout. It has a property row and column to organize children horizontally and vertically respectively. The default flexDirection is a column.
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { StyleSheet,View } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class FlexDirectionBasics extends Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <View style={styles.powderblue} />
- <View style={styles.skyblue} />
- <View style={styles.steelblue} />
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container:{
- flex: 1,
- flexDirection: 'row',// set elements horizontally, try column.
- },
- powderblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'powderblue',
- },
- skyblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'skyblue',
- },
- steelblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'steelblue',
- }
- })
Output
React Native Justify Content
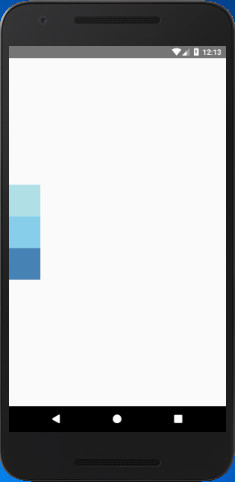
The justifyContent determines the distribution of children component along the primary axis. The children component are distributed at the start, end, center, or space evenly.
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { StyleSheet,View } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class JustifyContentBasics extends Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <View style={styles.powderblue} />
- <View style={styles.skyblue} />
- <View style={styles.steelblue} />
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container:{
- flex: 1,
- flexDirection: 'column', // set elements horizontally`.
- justifyContent: 'center',
-
- },
- powderblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'powderblue'
- },
- skyblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'skyblue',
- },
- steelblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'steelblue',
- }
- })
Output
React Native Align Items
The alignItems determine the alignment of children component along the secondary axis. If the primary axis is a column, then the secondary is a row, and when a primary axis is a row, then the secondary is a column. Using the alignItems, the children are aligned at start, end, center, or stretched.
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { StyleSheet,View } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class AlignItemsBasics extends Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View style={styles.container}>
- <View style={styles.powderblue} />
- <View style={styles.skyblue} />
- <View style={styles.steelblue} />
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- container:{
- flex: 1,
- flexDirection: 'column', // set elements horizontally`.
- justifyContent: 'center',
- alignItems: 'stretch',
- },
- powderblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'powderblue'
- },
- skyblue:{
- width: 60,
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'skyblue',
- },
- steelblue:{
- /*width: 60,*/
- height: 60,
- backgroundColor: 'steelblue',
- }
- })
Output
Note: The stretch does not work if the children have a fixed dimension along the secondary axis. In above example, the alignItems: stretch will not work until we remove width: 50.

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.