The ProgressBarAndroid component of React Native is used to indicate the progress status of some activity or app loading something. ProgressBarAndroid component works only on Android platform. To use the progress bar in iOS platform, a ProgressViewIOS component is used.
Props of ProgressBarAndroid
| Props | Type | Required | Description |
|---|
| animating | bool | no | It is used to show or hide the progress bar. Its default value is true to show, (false to hide). |
| color | color | no | It sets the color of progress bar. |
| indeterminate | indeterminateType | no | It shows the intermediate progress status of progress bar. It can only be false if the styleAtte of progress bar is Horizontal. |
| progress | number | no | It is a progress value between 0 and 1. |
| styleAttr | enum | no | It sets the style of progress bar. There are various style of progress bar in React Native such as Horizontal, Normal (default), Small, Large, Inverse, SmallInverse, and LargeInverse. |
| testID | string | no | It is used to locate this view in end-to-end tests. |
React Native ProgressBarAndroid Example
In this example, we will implement horizontal ProgressBarAndroid and perform action on TouchableOpacity component. The progress status will display in Text component up to 3 digits only.
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { Platform, StyleSheet, View, Text, TouchableOpacity, ProgressBarAndroid, ProgressViewIOS } from 'react-native';
- export default class MyApp extends Component<{}>{
- constructor() {
- super();
- this.state = {
- progressStatus: 0,
- }
- }
-
- start_Progress = () => {
- this.value = setInterval( () => {
- if(this.state.progressStatus <= 1){
- this.setState({progressStatus: this.state.progressStatus+ .01})
- }
- }, 100 );
- }
-
- stop_Progress = () =>{
- clearInterval(this.value);
- }
-
- clear_Progress =()=>{
- this.setState({progressStatus : 0.0})
- }
-
- render()
- {
- return(
- <View style = { styles.MainContainer }>
- <Text style = {{fontSize: 20, color: '#000'}}> Progress Value: { parseFloat((this.state.progressStatus * 100).toFixed(3))} %</Text>{
- ( Platform.OS === 'android' )
- ?
- ( <ProgressBarAndroid styleAttr = "Horizontal" progress = { this.state.progressStatus } indeterminate = { false } /> )
- :
- ( <ProgressViewIOS progress = { this.state.progressStatus } /> )
- }
- <TouchableOpacity activeOpacity = { 1 } style = { styles.button } onPress = { this.start_Progress }>
- <Text style = { styles.TextStyle }> Start Progress </Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- <TouchableOpacity activeOpacity = { 1 } style = { styles.button } onPress = { this.stop_Progress }>
- <Text style = { styles.TextStyle }> Stop Progress </Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- <TouchableOpacity activeOpacity = { 1 } style = { styles.button } onPress = { this.clear_Progress }>
- <Text style = { styles.TextStyle }> Reset Progress </Text>
- </TouchableOpacity>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
-
- const styles = StyleSheet.create(
- {
- MainContainer:
- {
- flex: 1,
- justifyContent: 'center',
- paddingTop: ( Platform.OS === 'ios' ) ? 20 : 0,
- margin: 20
- },
-
- button: {
- width: '100%',
- backgroundColor: '#00BCD4',
- borderRadius:5,
- padding: 10,
- marginTop: 10,
-
- },
-
- TextStyle:{
- color:'#fff',
- textAlign:'center',
- fontWeight: 'bold',
- }
- });
Output:
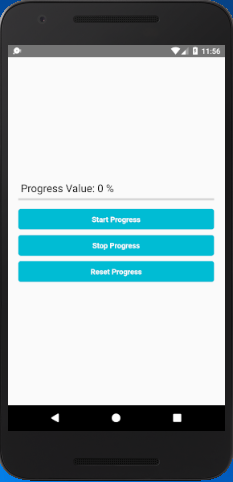
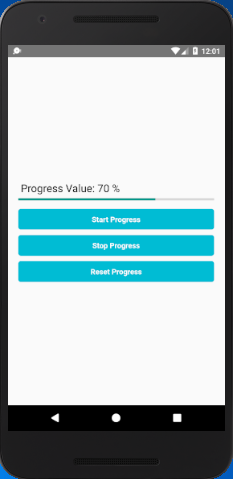
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.