React Native StatusBar is a component which is used to decorate status bar of the app. It is used by importing the StatusBar component from the react-native library. We can use multiple StatusBar at the same time.
React Native StatusBar Props
| Props | Description |
|---|---|
| animated | A status bar is animated if its property is changed. It supports backgrondColor, hidden, and barStyle. |
| barStyle | It sets the color of status bar text. |
| hidden | It is used to hide and show the status bar. By default, it is false. If hidden = {false} it is visible, if hidden = {true}, it hide the status bar. |
| backgroundColor | It sets the background color of the status bar. |
| translucent | When it is set of true, the app is built under the status bar. |
| showHideTransition | It displays the transition effect when showing and hiding the status bar. The default is 'fade'. |
| networkActivityIndicatorVisible | It checks the network activity indicator is visible or not. It supports in iOS. |
React Native StatusBar Methods
| setHidden | setBarStyle | setBackgroundColor |
| setNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible | setTranslucent |
React Native StatusBar Example 1
Let's create a simple StatusBar example in which we change its background color.
App.js
Output:
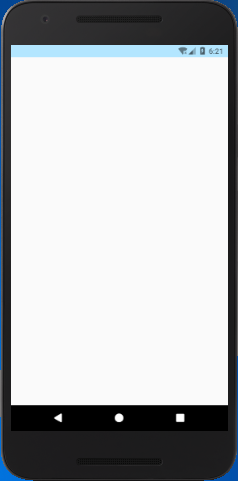
React Native StatusBar Example 2 (hiding status bar, full screen)
In this example, we hide the StatusBar by using its property hidden = true. Hiding the StatusBar makes the display as full-screen.
Output:

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.