React Native simply uses JavaScript for styling our core components. We don't require any special language or syntax for defining styles. All the core components use a prop (property) named style. The style names and values are similar to CSS that works for the web. There is the only difference in the way of writing names using camel casing, e.g fontSize rather than font-size.
The style prop is a plain old JavaScript object which is the simplest way for styling our code.
There are different ways to design our component, by using inline style and by using StyleSheet.create. As the component increases in complexity, it is better to use StyleSheet.create to define several styles in one place.
React Native style Example 1
In this example, we will use both inline style as well as StyleSheet.create. Inline styles are applied at where the components are created.
App.js
- import React, { Component } from 'react';
- import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
-
- export default class ImplementingStyle extends Component {
- render() {
- return (
- <View>
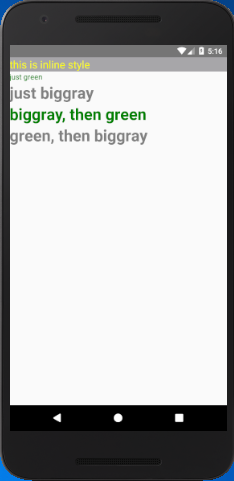
- <Text style={{ backgroundColor: '#a7a6a9', color: 'yellow', fontSize: 20 }}>this is inline style</Text>
- <Text style={styles.green}>just green</Text>
- <Text style={styles.biggray}>just biggray</Text>
- <Text style={[styles.biggray, styles.green]}>biggray, then green</Text>
- <Text style={[styles.green, styles.biggray]}>green, then biggray</Text>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
- const styles = StyleSheet.create({
- biggray: {
- color: 'gray',
- fontWeight: 'bold',
- fontSize: 30,
- },
- green: {
- color: 'green',
- },
- });
Output
React Native style Example 2
We can also use the external JavaScript file to style our application. In this example, we create external JS file and import it into our App.js file.
StyleComponent.js
- import React, { Component } from 'react'
- import { Text, View, StyleSheet } from 'react-native'
-
- const StyleComponent = (props) => {
- return (
- <View>
- <Text style = {styles.myState}>
- {props.myState}
- </Text>
- </View>
- )
- }
- export default StyleComponent
-
- const styles = StyleSheet.create ({
- myState: {
- marginTop: 20,
- textAlign: 'center',
- color: 'green',
- fontWeight: 'bold',
- fontSize: 20
- }
- })
App.js
- import React from 'react';
- import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
- import StyleComponent from './StyleComponent'
-
- export default class App extends React.Component {
- state = {
- myState: 'This is my state, style through external style'
- }
- render() {
- return (
- <View>
- <StyleComponent myState = {this.state.myState}/>
- </View>
- );
- }
- }
Output

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.