Most users interact with mobile through touches. There are combinations of gestures that work on it, such as tapping on the button, zooming the map, scrolling a list, etc. A button is one of the components that work on its click.
React Native Button is a basic component that works by clicking on it. It imports the Button class of react-native.
Props of Button
| Prop | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| onPress | function | yes | Call the handler when user clicks the button. |
| title | string | yes | Display the text inside the button. |
| accessibilityLabel | string | no | Display the text for blindness accessibility features. |
| color | Color | no | Set the background color of the Android button or set the color of iOS text. |
| disabled | bool | no | It disables all interactions for this component, if true. |
| textID | string | no | Used to locate this view in end-to-end tests. |
| hasTVPreferredFocus | bool | no | It preferred TV focus work only for Apple TV. |
React Native Button Example
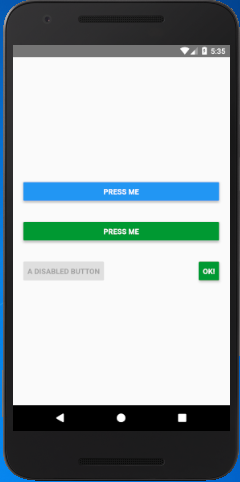
In this example, we will work on the button component. React Native Button component imports the Button class of react-native library. It has several props such as title, onPress, accessibilityLabel, etc. which are mentioned above.
In the previous article Positioning Element with Flex, we learned how to position elements in View.
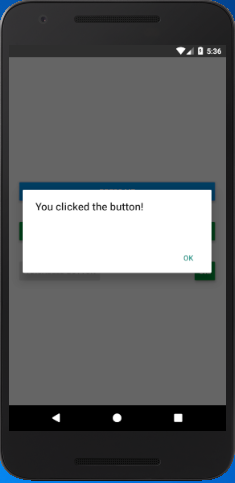
In the below code the title prop sets the title of a button, onPress prop calls the mention function and performs an event. The color prop sets the color of the button, and disabled={true} makes the button to disable.
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You.